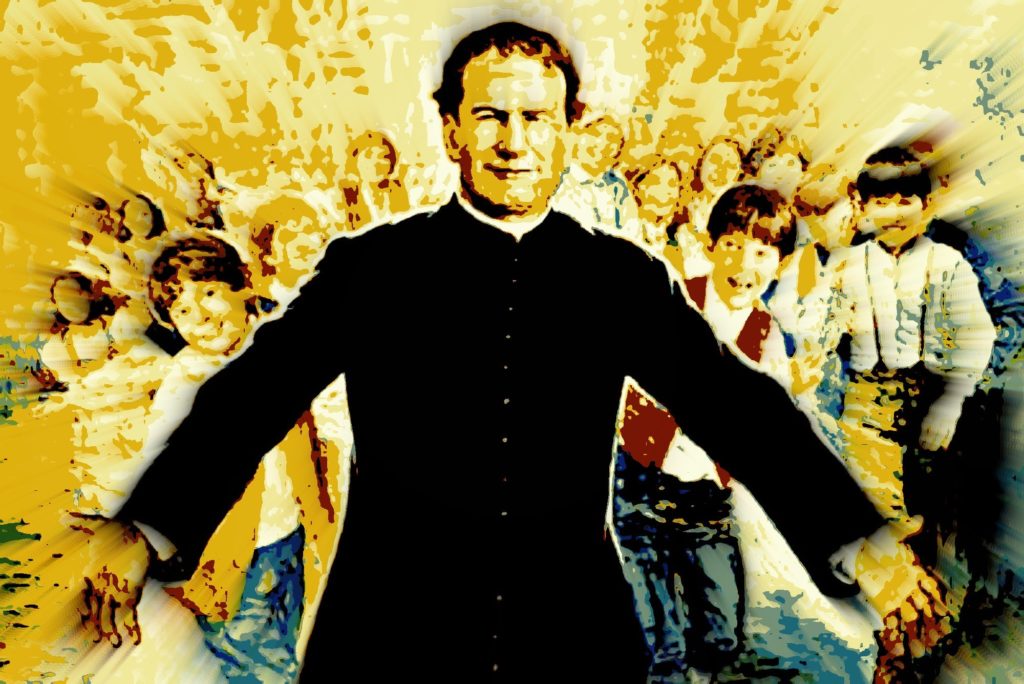
John Bosco (Italian: Giovanni Melchiorre Bosco; 16 August 1815 – 31 January 1888), popularly known as Don Bosco, was an Italian Roman Catholic priest of the Latin Church, educator and writer of the 19th century.
Don Bosco
While working in Turin, where the population suffered many of the effects of industrialization and urbanization, he dedicated his life to the betterment and education of street children, juvenile delinquents, and other disadvantaged youth. He developed teaching methods based on love rather than punishment, a method that became known as the Salesian Preventive System. A follower of the spirituality and philosophy of Saint Francis de Sales, Bosco dedicated his works to him when he founded the Salesians of Don Bosco, based in Turin. Together with Maria Domenica Mazzarello, he founded the Institute of the Daughters of Mary Help of Christians, a religious congregation of nuns dedicated to the care and education of poor girls.
In 1876 Bosco founded a movement of laity, the Association of Salesian Cooperators, with the same educational mission to the poor. In 1875 he began to publish the Salesian Bulletin. The Bulletin has remained in continuous publication, and is currently published in 50 different editions and 30 languages
Bosco established a network of organizations and centres to carry on his work. Following his posthumous beatification in 1929, he was canonized as a saint in the Roman Catholic Church by Pope Pius XI in 1934.